Run a NodeJS process through forever from within a Docker container
linux docker open-source operations procedure webplatform - 📁 projects
Specification Document for RangeFinder API
One of the components that I worked on during my time on the WebPlatform project, Publican, that I had to manage has many moving parts. The end product of that component is basically static HTML documents that ends up on specs.webplatform.org.
Since we need to have many packages installed in very specific version, and automating the installation wouldn't bring any more benefit than being self-contained, I thought it would be best to go through the steps of converting it into a Docker container.
The following is a procedure I wrote to teach my colleague, Robin Berjon, how to run his system called Publican from within a Docker container. Publican is basically a GitHub hook listener that generates specs written to be parsed by ReSpec or Bikeshed
Run publican inside Docker
What this'll do is basically build a VM that'll run a Docker container. The container will write in files outside of it.
You'll quickly notice that the paths will look the same, its confusing, sorry
about that. Fortunately for us, the paths in the procedure are the ones that
will be mounted through Docker Volume (the -v option when you call docker)
and will, in the end, be the same files.
Once you have a Docker container running on a VM, it'll replicate how a production VM will run the tasks. Since we know where the container will write files, we'll have our frontend servers to forward requests to publican, and serve files it generated.
Doing all this removes the need to do any rsync. NGINX within the VM that'll run Docker will take care of serving static files, and frontend server will expose it to the public.
Steps
- Have Vagrant and VirtualBox installed
- Follow what's in renoirb/salt-basesystem README.md
-
Make sure you follow Vagrant Sandbox utilities part
vagrant ssh sudo salt-call state.highstate sudo salt-call state.sls vagrantsandbox.docker exit -
Reboot the VM by doing
vagrant reloadvagrant reload
-
No need to follow what's in webplatform/publican DOCKER.md file. Those are notes to show how to build a container. For this time, we'll use a container I already built and pushed on Docker hub!
-
Setup what's required to run the container
vagrant ssh
-
Prepare the folders;
sudo -s su webapps id -
You should see
uid=990(webapps) gid=990(webapps) groups=990(webapps),33(www-data),998(docker) -
Prepare the folders
cd /srv/webapps mkdir publican/data cd publican-
If all went well so far; you should be able to do
docker psas thewebappsuser. Otherwise reboot and/or runsalt-callwith bothstate.highstatestate.sls vagrantsandbox.dockerstates. There should be nothing left to do.docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED ...
-
-
Pull the publican Docker image I built (it'll take about 10 minutes)
docker pull webspecs/publican:wip
- Copy the other files in this Gist in your local coputer where you cloned the salt-basesystem repository. From that folder you can move them inside the Vagrant VM where you need.
-
Copy publican config
cp /vagrant/config.json data/ -
Download Bikeshed stuff that i didn't figure out yet what's important to keep, extract it in./srv/webapps/publican/spec-data/
-
You can open up another terminal session and connect to the Vagrant VM
vagrant ssh(e.g. if you don't usetmuxorscreen)mkdir -p spec-data/readonly/ mkdir -p data/{gits,logs,publish,queue,temp}
-
Run the container
docker run -it --rm -v "$(pwd)/data":/srv/webapps/publican/data \ -v "$(pwd)/spec-data":/opt/bikeshed/bikeshed/spec-data \ -p 7002:7002 webspecs/publican:wip
-
If you see the following, you're in the Docker container!!
webapps@2f33f5c6e183:~$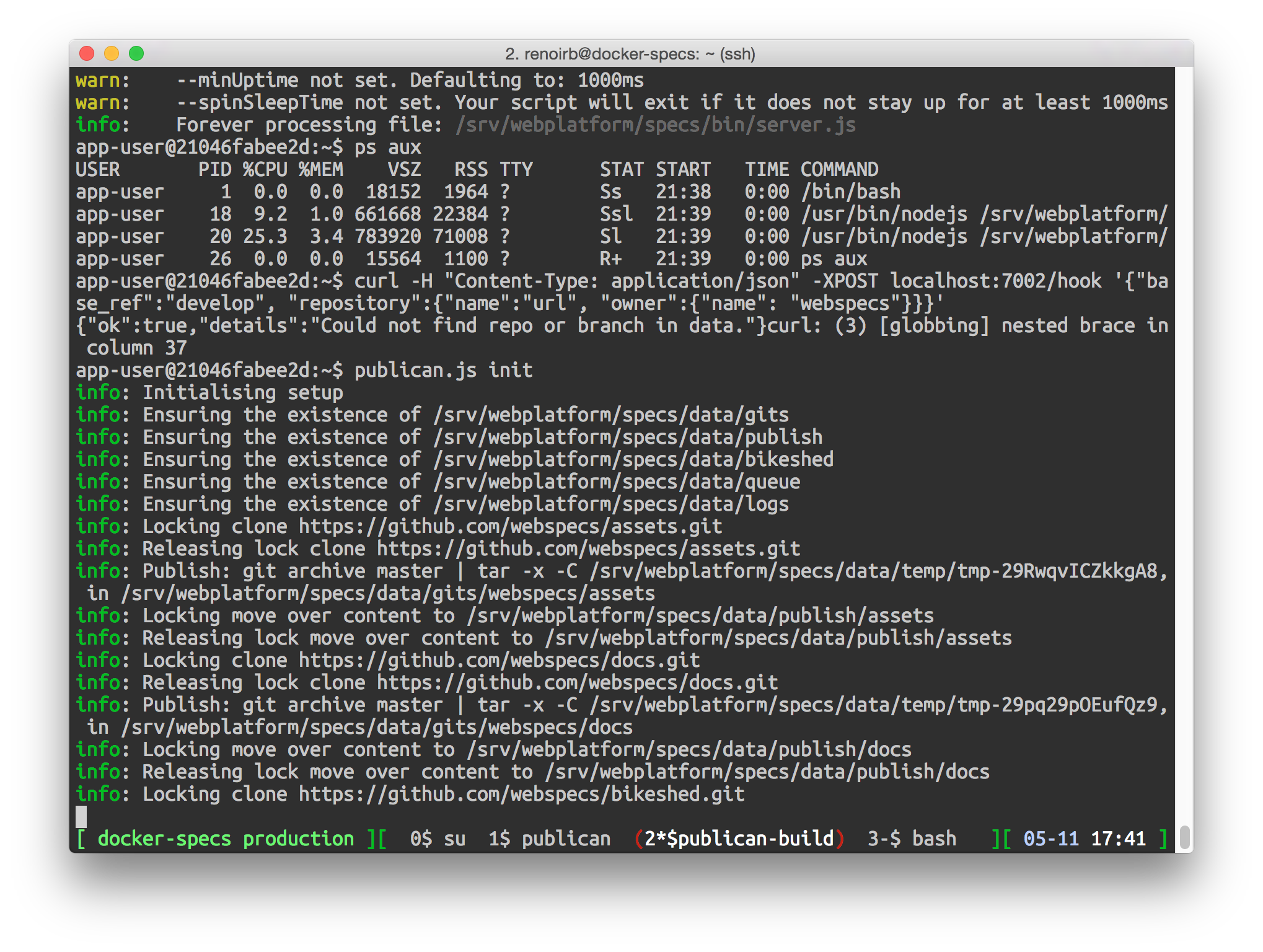
Launching the container -
Initiate the empty shell we just created (it'll create stuff in the
data/folder outside of the container)
publican.js init
-
It should look like the screenshot with caption "Launching the container".
-
Once done, exit the container. Notice that by doing this, you lose the state of the VM and anything that has been written in the container. But, since we use volumes (notice the
-v /host/path:/container/path), we actually wrote outside of the container. -
We can exit the container
exit -
At this stage, we had publican and bikeshed to generate files (we may call this a "cache warmup" of softs). Now, let's prepare the Vagrant VM to serve the static content. Notice that the next commands are there only for the purpose of a local workspace, in production this step will also be managed automatically.
-
Let's get back as the root user, and create a quick web server;
exit apt-get -yqq install nginx mv /vagrant/default.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available/default service restart nginx -
Let's return back to as the webapps user and launch the runner
su webapps cd /srv/webapps/publican/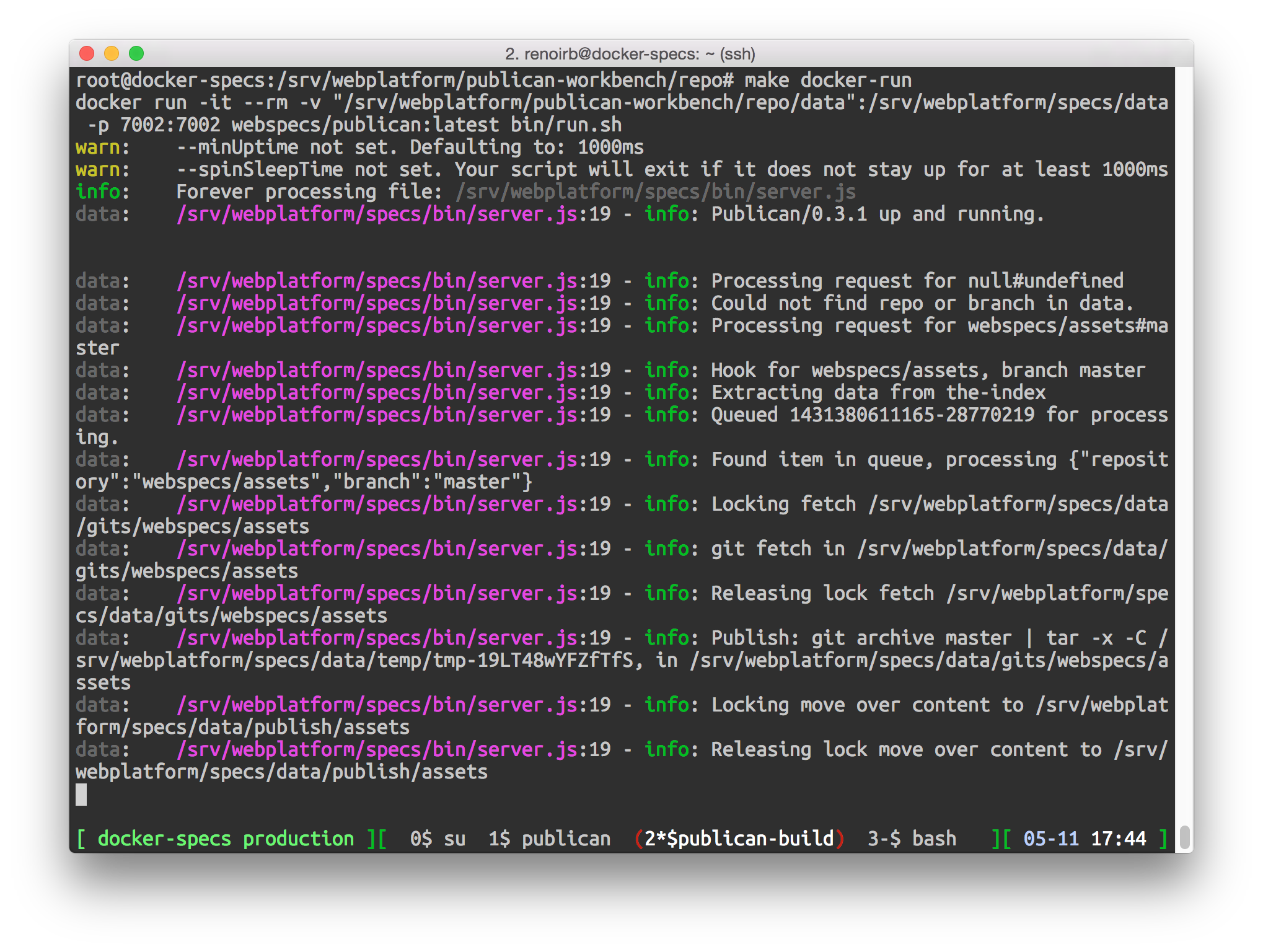
Starting a build process -
Starting a build process; this will also be managed automatically in production.
docker run -it --rm -v "$(pwd)/data":/srv/webapps/publican/data \
-v "$(pwd)/spec-data":/opt/bikeshed/bikeshed/spec-data \
-p 7002:7002 webspecs/publican:wip
It should look like the screenshot with caption "Starting a build process".
-
get your Vagrant VM IP address
ifconfig -
Should start by
172...or192...; visit a browser to that address
Gists
Here are the files mentioned in this post
config.json
Publican expects this file as data/config.json.
{
"bikeshed": "/opt/bikeshed/bikeshed.py",
"rsyncPath": "/srv/webapps/publican/",
"python": "python2",
"logFile": "logs/all.log",
"email": {
"to": "jdoe@example.org",
"from": "jdoe@example.org",
"host": "localhost",
"level": "error",
"handleExceptions": true
},
"purgeAllURL": "https://api.fastly.com/service/fooo/purge_all",
"purgeAllKey": "baar"
}
default.conf
A minimal NGINX web server digging for static content that Publican generates.
# file: /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
server {
listen 80 default_server;
root /srv/webapps/publican/data/publish;
index index.html index.htm;
server_name localhost;
location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; }
}
Dockerfile
Here is the project's Dockerfile I created. I think it should be smaller, but Publican works with the following script.
Each step in a Dockerfile creates a "commit", make sure you have as few of them as possible, and also make sure that you clean after yourself. Remember that a Docker container is re-deployable and smallest the size of the container, the better!
Notice a few details;
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractivehelps with dialogsUSER webappstells "where" the rest of the script will make commands as a different user than root. Make sure what's required by root to be done before!COPY ...this is basically how you import content inside the container (i.e. make the container heavier)
#
# Publican Docker runner
#
# See also:
# * https://github.com/nodesource/docker-node/blob/master/ubuntu/trusty/node/0.10.36/Dockerfile
FROM nodesource/trusty:0.10.36
MAINTAINER Renoir Boulanger <renoir@w3.org>
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
# Dependencies: Bikeshed, PhantomJS, Bikshed’s lxml
RUN apt-get update && apt-get -y upgrade && \
apt-get install -yqq git python2.7 python-dev python-pip libxslt1-dev libxml2-dev zlib1g-dev && \
apt-get install -yqq libfontconfig1 libfreetype6 curl && \
apt-get autoremove -yqq --purge && \
pip install --upgrade lxml
# Copy everything we have locally into the container
# REMINDER: Make sure you run `make clone-bikeshed`, we prefer to keep a copy locally outside
# of the data volume. Otherwise it would make problems saying that bikeshed clone is not in the
# same filesystem.
COPY . /srv/webapps/publican/
# Make sure we have a "non root" user and
# delete any local workbench data/ directory
RUN /usr/sbin/groupadd --system --gid 990 webapps && \
/usr/sbin/useradd --system --gid 990 --uid 990 -G sudo --home-dir /srv/webapps --shell /bin/bash webapps && \
sed -i '/^%sudo/d' /etc/sudoers && \
echo '%sudo ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL' >> /etc/sudoers && \
mv /srv/webapps/publican/bikeshed /opt && \
rm -rf data && \
mkdir -p data/temp && \
rm -rf Dockerfile Makefile .git .gitignore DOCKER.md && \
chown -R webapps:webapps /srv/webapps/publican && \
chown -R webapps:webapps /opt/bikeshed
# Switch from root to webapps system user
# It **HAS to be** the SAME uid/gid as the owner on the host from which we’ll use as volume
USER webapps
# Where the session will start from
WORKDIR /srv/webapps/publican
# Environment variables
ENV PATH /srv/webapps/publican/node_modules/.bin:/srv/webapps/publican/bin:/srv/webapps/publican/.local/bin:$PATH
ENV HOME /srv/webapps/publican
ENV TMPDIR /srv/webapps/publican/data/temp
ENV NODE_ENV production
ENV GIT_DISCOVERY_ACROSS_FILESYSTEM true
# Run what `make deps` would do
RUN pip install --upgrade --user --editable /opt/bikeshed && \
mkdir -p node_modules && npm install
# Declare which port we expect to expose
EXPOSE 7002
# Allow cli entry for debug, but make sure docker-compose.yml uses "command: bin/run.sh"
ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/bash"]
# Note leftover: Ideally, it should exclusively run
#ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/bash", "/srv/webapps/publican/bin/run.sh"]
# Note leftover: What it ends up doing
#CMD ["node_modules/forever/bin/forever", "--fifo", "logs", "0"]
Forever start script
If you notice in the Docker run command, I call a file bin/run.sh, here it is.
docker run -it \
--rm \
-p 7002:7002 \
webspecs/publican:latest \
bin/run.sh
Publican runs its process using Forever. The objective of forever is to keep a process to run at all times.
While this isn't ideal for NodeJS services, in the present use-case of a Docker container who has the only purpose to run a process; Forever apt for the job!
#!/bin/bash
export RUNDIR="/srv/webapps/publican"
cd $RUNDIR
node_modules/forever/bin/forever start $RUNDIR/bin/server.js
node_modules/forever/bin/forever --fifo logs 0
That’s it, it’s all I had.